How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to precision surveying. This guide provides a step-by-step approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and essential maintenance. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your existing skills, we’ll equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
We’ll explore the intricacies of drone components, explaining their functions and how they work together to achieve flight. You’ll learn about essential pre-flight procedures to ensure safe operation, covering legal requirements and practical checks. We’ll then delve into the art of piloting, guiding you through basic and advanced flight maneuvers, including techniques for navigating challenging conditions. Finally, we’ll cover crucial aspects like drone maintenance, battery management, and understanding relevant regulations, ensuring your drone operation remains safe, legal, and enjoyable.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating this process requires understanding regulations and safety procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including practical exercises and troubleshooting, refer to this excellent resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight. Safe and responsible drone operation is paramount for both the operator and the surrounding environment.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the different parts of your drone and the terminology used is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will detail the key components and define common terms, helping you navigate the world of drone technology with confidence.
Major Drone Components and Their Functions
A drone’s functionality relies on the coordinated operation of several key components. Let’s explore their individual roles:
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate the thrust needed for lift and maneuverability. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust, efficiency, and noise.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into rotational motion. Brushless motors are commonly used in drones due to their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: This is the drone’s “brain,” responsible for processing sensor data and controlling the motors to maintain stability and execute commands. It integrates inputs from various sensors, like gyroscopes and accelerometers.
- Battery: Provides the power source for all drone components. The battery’s capacity (measured in mAh) directly impacts flight time.
- GPS Module (optional): Many drones include a GPS module for precise positioning, enabling features like autonomous flight modes and return-to-home functionality.
- Radio Transmitter/Controller: Allows the pilot to control the drone’s movements and access various flight modes. This device communicates wirelessly with the drone’s flight controller.
- Camera (optional): Many drones are equipped with cameras for capturing aerial photos and videos. Camera specifications vary widely, impacting image quality and features.
Drone Terminology Glossary
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terminology will enhance your understanding of drone operation and maintenance. Here’s a quick glossary:
- LiPo: Lithium Polymer battery, a common type of rechargeable battery used in drones.
- mAh: Milliampere-hour, a unit of measurement for battery capacity.
- ESC: Electronic Speed Controller, regulates the power supplied to each motor.
- IMU: Inertial Measurement Unit, a sensor system that measures acceleration and rotation.
- GPS: Global Positioning System, used for location and navigation.
- RTF: Ready-To-Fly, a drone that comes fully assembled and ready to operate.
- FPV: First-Person View, a system that allows the pilot to see what the drone’s camera sees.
Comparison of Drone Battery Types

Different battery types offer various advantages and disadvantages. The choice depends on factors such as flight time requirements, budget, and performance needs.
| Battery Type | Pros | Cons | Typical Flight Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo (Lithium Polymer) | High power density, lightweight | Requires careful handling, can be expensive, limited cycle life | Varies greatly depending on capacity and drone model (e.g., 15-30 minutes) |
| LiFe (Lithium Iron Phosphate) | Safer than LiPo, longer cycle life | Lower power density, heavier | Generally shorter than LiPo batteries of similar weight |
| LiHV (Lithium Polymer High Voltage) | Higher voltage than standard LiPo, increased flight time | Requires compatible charger and ESC, can be more expensive | Longer than standard LiPo batteries |
| NiMH (Nickel-Metal Hydride) | Relatively inexpensive, safe | Lower energy density, heavier, shorter flight times | Significantly shorter than LiPo batteries |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for safe and responsible drone operation. Neglecting these checks can lead to accidents or malfunctions. This section Artikels a comprehensive pre-flight procedure.
Comprehensive Pre-Flight Checklist

Before each flight, systematically check the following:
- Battery Level: Ensure the battery is fully charged and has sufficient charge for the planned flight duration. Check the voltage using a battery checker for LiPo batteries.
- Propeller Tightness: Verify that all propellers are securely fastened to the motors. Loose propellers can cause vibrations, instability, and potential failure.
- Radio Transmitter/Controller Check: Make sure the transmitter is powered on and properly paired with the drone. Check the battery level of the transmitter as well.
- GPS Signal (if applicable): Ensure the drone has a strong GPS signal before takeoff. This is crucial for features like autonomous flight and Return-to-Home.
- Visual Inspection: Carefully inspect the drone for any visible damage, loose parts, or debris. Pay close attention to the propellers, motors, and camera.
- Environmental Conditions: Check weather conditions, such as wind speed and direction. Avoid flying in strong winds or adverse weather.
- Airspace Restrictions: Verify there are no airspace restrictions in your intended flight area using apps like B4UFLY or similar tools. Always check local regulations.
- Emergency Procedures Familiarity: Review your emergency procedures in case of loss of signal, low battery, or other unexpected events.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe and controlled takeoff and landing procedures are critical for preventing accidents and damage. This section Artikels best practices for both.
Safe Takeoff Procedure, How to operate a drone
Follow these steps for a controlled takeoff:
- Perform all pre-flight checks.
- Select an open, level area away from obstacles and people.
- Power on the transmitter first, then the drone.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (if necessary), as per the drone’s manual.
- Slowly increase throttle to initiate liftoff, maintaining a steady ascent.
- Once airborne, perform a short hover test to ensure stability.
Safe Landing Procedure
Smooth landings are essential to avoid damage to the drone. Here’s how:
- Begin descent slowly, gradually reducing throttle.
- Maintain a steady descent rate, avoiding sudden drops.
- In windy conditions, adjust your approach to compensate for wind gusts.
- Once close to the ground, gently lower the drone to a soft landing.
- Power off the drone, then the transmitter.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques
Many drones offer assisted takeoff and landing (ATOL) features. These automated functions simplify the process, particularly for beginners. However, understanding manual takeoff and landing is still crucial for handling unexpected situations.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding basic flight controls is fundamental to operating a drone safely and effectively. This section explains the functions of the control sticks and guides you through basic maneuvers.
Flight Control Stick Functions
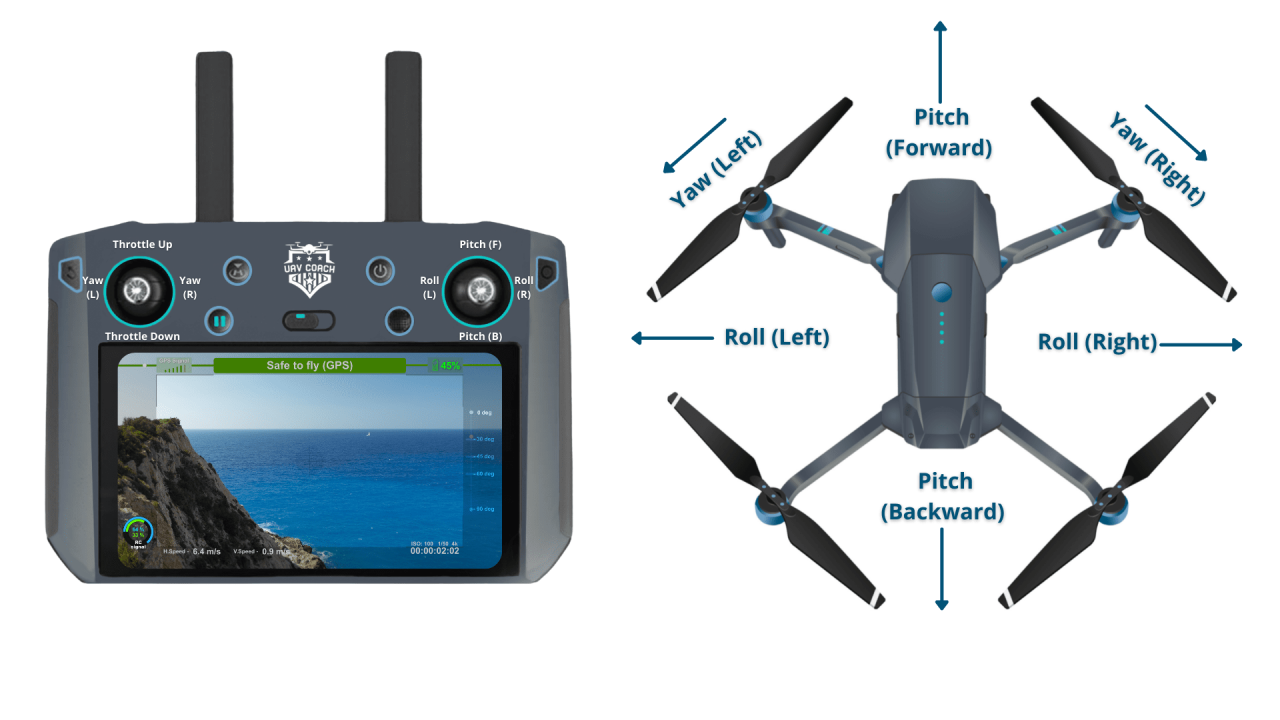
Most drone controllers use two sticks to control the drone’s movements:
- Left Stick (Yaw/Throttle): Vertical movement controls throttle (up for ascent, down for descent). Horizontal movement controls yaw (left/right rotation).
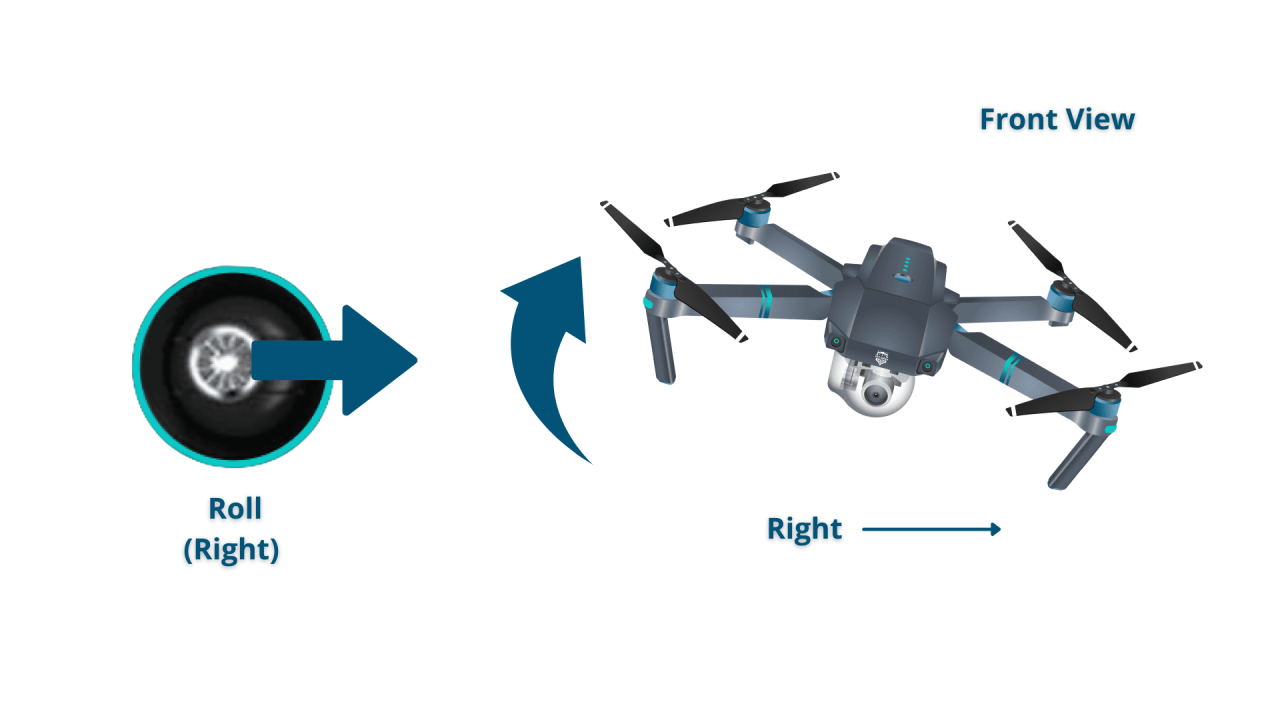
- Right Stick (Pitch/Roll): Forward/backward movement controls pitch (forward/backward tilt). Left/right movement controls roll (left/right tilt).
Basic Flight Maneuvers
Practice these maneuvers in a safe, open area:
- Hovering: Maintain a stable position in the air.
- Moving Forward/Backward: Gently push the right stick forward or backward.
- Moving Sideways: Gently push the right stick left or right.
- Rotating (Yaw): Gently push the left stick left or right.
Common Beginner Mistakes
Beginners often make these mistakes; avoid them by practicing and paying attention:
- Sudden movements: Avoid jerky inputs; use smooth, controlled movements.
- Ignoring wind conditions: Account for wind when maneuvering the drone.
- Flying too close to obstacles: Maintain a safe distance from obstacles and people.
- Neglecting battery level: Always monitor battery level and land before it gets too low.
Advanced Flight Techniques
As you gain experience, you can explore more advanced flight techniques. Mastering these will enhance your drone piloting skills and allow for more creative aerial shots.
Complex Maneuvers and Emergency Procedures
Advanced maneuvers require practice and a good understanding of your drone’s capabilities. These include precise hovering in challenging conditions, flying in strong winds, and executing emergency procedures such as controlled emergency landings in case of a loss of control or low battery.
GPS and Autonomous Flight Modes
GPS-enabled drones offer various autonomous flight modes, such as:
- Altitude Hold: Maintains a constant altitude.
- Position Hold: Maintains a fixed position in space.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): Automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point.
- Waypoints: Allows you to program a flight path for the drone to follow autonomously.
Effective Use of Flight Modes
Understanding and utilizing different flight modes effectively enhances your control and allows for more complex shots. For instance, altitude hold is ideal for stable aerial photography, while position hold allows for precise positioning over a subject. Waypoints are useful for capturing complex aerial shots and time-lapses.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Many drones are equipped with cameras, opening up possibilities for stunning aerial photography and videography. This section explains how to optimize your camera settings and capture high-quality content.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture significantly impact image quality. Experiment to find the optimal settings for different lighting conditions:
- ISO: Controls the camera’s sensitivity to light. Lower ISO values result in less noise but require more light.
- Shutter Speed: Determines how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds can create motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the size of the lens opening, affecting depth of field. A wider aperture (lower f-number) results in a shallower depth of field, blurring the background.
Camera Modes and Applications
Different camera modes offer various creative options:
- Photo Mode: Captures still images.
- Video Mode: Records moving images.
- Timelapse Mode: Captures a sequence of images at set intervals, which can be combined to create a time-lapse video.
Tips for High-Quality Aerial Media
Capture stunning aerial photos and videos by considering these factors:
- Composition: Utilize the rule of thirds and leading lines to create visually appealing shots.
- Framing: Carefully choose your angles and perspectives to highlight your subject.
- Lighting: Shoot during the golden hours (sunrise and sunset) for optimal lighting conditions.
- Steady Shots: Avoid sudden movements to prevent shaky footage.
Drone Maintenance and Safety
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring your drone’s longevity and safe operation. This section provides a maintenance schedule and troubleshooting tips.
Drone Maintenance Schedule
Establish a regular maintenance routine, including:
- Cleaning: Regularly clean the drone’s body and propellers to remove dirt and debris.
- Inspection: Inspect the drone for any signs of damage or wear and tear after each flight.
- Component Replacement: Replace worn-out or damaged components as needed, such as propellers and batteries.
- Firmware Updates: Keep your drone’s firmware updated to benefit from bug fixes and new features.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Addressing common issues promptly can prevent serious problems. Examples include motor malfunctions (check motor connections and ESC settings), GPS signal loss (check for obstructions and ensure GPS is enabled), and battery issues (check battery voltage and charging).
Safe Storage and Transportation
Store your drone and accessories in a safe, dry place, away from extreme temperatures. Use a protective case during transportation to prevent damage.
Battery Management and Charging
Proper battery care is essential for maximizing battery lifespan and ensuring safe operation. This section details safe charging procedures and best practices.
Importance of Proper Battery Care
LiPo batteries have a limited number of charge cycles. Proper care extends their lifespan. Avoid overcharging, deep discharging, and extreme temperatures.
Safe Charging Procedures
Always use the appropriate charger for your battery type. Never leave batteries unattended while charging and avoid overcharging. Use a balance charger for LiPo batteries to ensure even cell charging.
Battery Charging Methods
Different charging methods exist, each with its impact on battery health. Faster charging methods may reduce the battery’s lifespan, while slower methods may be gentler.
Understanding Drone Regulations and Laws: How To Operate A Drone
Operating a drone legally is crucial. This section highlights key regulations and the importance of compliance.
Key Regulations and Laws
Regulations vary by location. Familiarize yourself with the specific laws in your area regarding drone operation, including airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and permitted flight zones.
Drone Registration and Permits
In many regions, registering your drone and obtaining necessary permits is mandatory. Failure to comply can result in fines or legal repercussions.
Consequences of Violating Regulations
Violating drone regulations can lead to fines, legal action, and even criminal charges, depending on the severity of the violation.
Emergency Procedures and Troubleshooting
Being prepared for emergencies is crucial for safe drone operation. This section details procedures for handling various emergency situations.
Handling Emergency Situations
Situations like low battery warnings, loss of signal, or unexpected malfunctions require immediate action. Knowing how to react calmly and efficiently is critical.
Safe Drone Recovery After a Crash
If a crash occurs, prioritize safety. Assess the situation, secure the area, and carefully recover the drone, ensuring no further damage or injuries occur. Inspect the drone for damage after recovery.
Decision-Making Process During a Drone Emergency
A structured approach is essential during an emergency. Prioritize safety, assess the situation, and take appropriate action based on the specific emergency.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical understanding and practical application. By following the comprehensive steps Artikeld in this guide, you’ll gain the confidence to handle your drone safely and efficiently. Remember that consistent practice, coupled with a thorough understanding of the regulations and safety procedures, is key to becoming a skilled and responsible drone pilot.
Embrace the learning process, enjoy the flight, and capture stunning aerial perspectives with confidence and expertise.
FAQ Resource
What is the best type of drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with features like GPS stabilization and assisted takeoff/landing are ideal for beginners. Research models with good reviews and ease-of-use ratings.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking to the skies, and a great resource to begin your journey is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This will help you confidently handle your drone and ensure safe and responsible operation.
Compass calibration should be performed before each flight, especially if you’ve transported your drone or experienced any significant magnetic interference.
What should I do if I lose signal with my drone?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If unavailable, try to manually guide it back, keeping a visual on the drone.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, usage (flight style and features used), and weather conditions. Check your specific drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.